User database revised
Contains changes to the User database design and API that are needed for subscription information and possibly other needs.
2010-09-13: Changes due to the introduction of a U_loginname field.
2010-09-14: Names of various methods are changed.
2010-09-24: Changes in the database structure. A row in the File table is now directly owned by a user. These changes are rendered in bold.
2010-09-28: Added the file_delete method.
2010-11-11: Removed WMS_URL and WMS_XML entries from the InfoDS table
Overview
Design
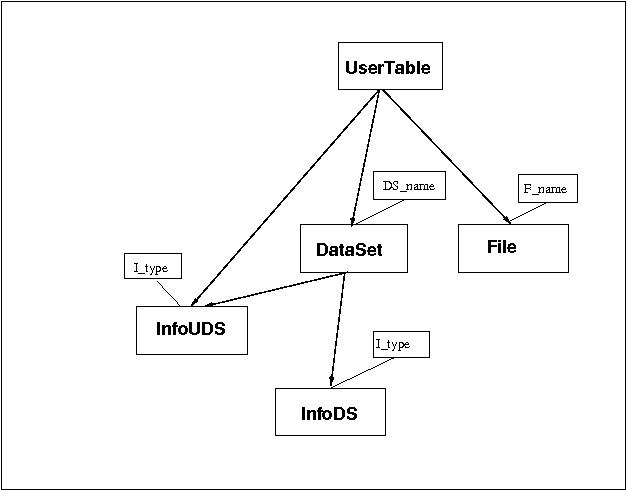
Database tables
UserTable
| U_id | A_id | U_name | U_email | U_loginname | U_password | U_institution | U_telephone | U_session |
DataSet
| DS_id | U_id | A_id | DS_name |
InfoDS
| I_id | DS_id | I_type | I_content |
InfoUDS
| I_id | U_id | DS_id | I_type | I_content |
File
| U_id | F_name | F_timestamp | F_size | F_status | F_errurl |
The table details are presented below:
UserTable
| U_id | Unique user id (autoincremented number). Primary key |
|---|---|
| A_id | Application id. Many METAMOD applications share the same database. This field has the same value as the APPLICATION_ID in the master_config.txt file. |
| U_name | User name as given in registration form |
| U_email | User E-mail address as given in registration form |
| U_loginname | Login name for user authentication |
| U_password | User password |
| U_institution | User institution acronym as given in registration form |
| U_telephone | User telephone number as given in registration form |
| U_session | User session id. Random string generated when the user initiate a new interactive session. |
The U_session field is used to track the state of an interactive user session. The user may only have one interactive session active at any time. If the user initiate a new session when another session is already active, the old session disappears. If the user tries to continue the old session, an error message will be submitted. This is the same mechanism used in the old (METAMOD 2.3 and earlier) file-based version.
The A_id field connects the user to one of the METAMOD applications that share the same database. If the same person wants to be a user of more than one of these METAMOD applications, she/he must apply for a user account in each application, and the database will contain independent rows in the user table, one for each application.
DataSet
| DS_id | Unique dataset id (autoincremented number). Primary key. Not same number as in the Metadata Database |
|---|---|
| U_id | Identifies the user owning the dataset. |
| A_id | Application id. |
| DS_name | Dataset name. Name of dataset as provided by the user. Not the same name as in the corresponding field in the Metadata Database. But the last part of the name found in the Metadata Database field (everything after '/') will correspond to this field. |
The combination of the A_id and DS_name fields will provide an alternative unique key that can be used to find a dataset without knowing the owning user.
InfoDS
This table is used to contain various information connected to a dataset. Each row has a serial unique identifier (I_id). The row is connected to a dataset through the DS_id foreign key.
A type tag (I_type) field tells what kind of information is contained in the row. The value is a short acronym for a limited set of information types. The piece of information is found in the I_content text field.
| I_id | Unique id (autoincremented number). Primary key |
|---|---|
| DS_id | Identifiles a dataset this info-row is connected to. |
| I_type | Type tag. Short acronym that identifies the information type. |
| I_content | The text string representing a piece of information. This can be a single entity (unstructured text) or an XML document. |
For the time being, the following information types (I_type) will be needed.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| DSKEY | Dataset key (also called directory key or dirkey) as provided by the user. Single entity |
| LOCATION | Location. Single entity. Absolute path to the directory under which all files belonging to the dataset are found. The files may be found directly in the location directory, or in any subdirectory of the location directory at any level. |
| CATALOG | Partial URL to a THREDDS dataset. Single entity. Combined with the file name, this URL can be used to access the content of a file through a TDS server. It can also provide the URL that points to the THREDDS catalog containing the METAMOD dataset. |
| Additional information types may be added later, for example to implement projection information: | |
| PROJECTION_XML | XML document used to represent reprojection information. The document contains, among other things, each projection the user has asked for (“Lat/Long”, “Stereo” etc.). Each projection contains attributes: method, projString, xAxis, yAxis and toDegree. |
InfoUDS
This table is used to express relationships between a dataset and a user. Each row has a serial unique identifier (I_id). The row is connected to a dataset through the DS_id foreign key, and to a user through the U_id foreign key.
A type tag (I_type) field tells what kind of information is contained in the row. The value is a short acronym for a limited set of information types. The piece of information is found in the I_content text field.
| I_id | Unique id (autoincremented number). Primary key |
|---|---|
| U_id | Identifiles a user this row is connected to. |
| DS_id | Identifiles a dataset this info-row is connected to. |
| I_type | Type tag. Short acronym that identifies the information type. |
| I_content | The text string representing a piece of information. This can be a single entity (unstructured text) or an XML document. |
For the time being, the following information types (I_type) will be needed.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| SUBSCRIPTION_XML | XML describing details of a subscription on the dataset set up by the user |
File
| U_id | User that this file belongs to. Part of primary key. |
|---|---|
| F_name | Local path to file. The full path is given by “LOCATION/F_name” where LOCATION is the dataset LOCATION found in the Info table. Part of primary key. |
| F_timestamp | Timestamp of last change |
| F_size | File size (bytes) |
| F_status | Status (OK or errors) |
| F_errurl | URL to error report (if errors) |
This table is used to display recent changes to the data provider. It will not contain a complete inventory of files in the repository. This table will be purged (rows with old timestamps removed) periodically.
API design
This paragraph defines a set of subroutine/function calls that are used to read and write information to/from the user database. These functions will be implemented in PHP and/or Perl as needed.
The functions are defined as methods in a Userbase class. Inside a Userbase object, there may be a current user and a current dataset. The current user may or may not own the current dataset. There may also be a current file that will belong to the current dataset.
Open/close functions
| Method | Purpose | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| new | Create a new Userbase object and set up a connection to the User database | OUT: Userbase object reference |
| close | Save any pending changes to the database, and close the connection | None |
| revert | Revert any changes to the database made by this Userbase object. Close the database connection. | None |
User functions
| Method | Purpose | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| user_find | Search for an existing user in the database and make him/her the current user. | IN: User E-mail address, application id (A_id). |
| user_lfind | Search for an existing user in the database and make him/her the current user. | IN: User login name, application id (A_id). |
| user_create | Create a new user and make it the current user. | IN: User E-mail address, application id (A_id). Initially, the value of the mandatory U_loginname field will be set to the E-mail address, but this can be changed using the user_set method. |
| user_put | Set user properties for the current user | IN: Property name (one of 'U_name', 'U_loginname', 'U_password', 'U_institution', 'U_telephone', 'U_session'), property value |
| user_get | Get user properties for the current user. | IN: Property name (one of 'U_id', 'U_email', 'A_id', 'U_name', 'U_password', 'U_loginname', 'U_institution', 'U_telephone', 'U_session'). OUT: property value |
| user_first | Make the first user in the database the current user. | OUT: TRUE if found, FALSE if no users exist. |
| user_next | Make the next user in the database the current one. | OUT: TRUE if found, FALSE if already last user. |
| user_isync | Make the user corresponding to the current infoUDS-row (see below) the current user. | OUT: TRUE if found, FALSE on error. |
| user_dsync | Make the user owning the current dataset the current user. | OUT: TRUE if found, FALSE on error. |
Dataset functions
Methods for manipulating the DataSet table.
| Method | Purpose | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| dset_create | Create a new dataset and make it the current dataset. The current user will be the owner of the new dataset. | IN: Dataset name, dataset key. |
| dset_find | Find a dataset in the database and make it the current dataset. | IN: Application id, dataset name. OUT: true if the dataset is found, false otherwise. |
| dset_first | Make the first dataset (owned by the current user) the current dataset | OUT: true if found, false if no such dataset exists. |
| dset_next | Make the next dataset (owned by the current user) the current dataset. | OUT: true if found, false if already last dataset. |
| dset_isync | Make the dataset corresponding to the current infoUDS-row (see below) the current dataset. | OUT: TRUE if found, FALSE on error. |
| dset_get | Get information from the current dataset. | IN: Information type (I_type) or one of 'ds_name', 'ds_id', 'u_id'. OUT: Value of I_content field (single entity or XML). |
| dset_put | Add or replace content fields in the current dataset. | IN: Information type (I_type), value of I_content field (single entity or XML). |
Functions for manipulating the InfoUDS table
Uses the concept “current set of InfoUDS rows”. This set is a subset of the rows in the InfoUDS table given by how the rows are connected to the current user and/or the current dataset. In addition, all rows in the current set must represent the same information type (I_type). One of the rows in the current set may be selected as the current infoUDS row.
| Method | Purpose | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| infoUDS_set | Define the current set of rows and set the first row in as the current row. | IN: 1. Information type. 2. Keyword that tells how the set shall relate to the current user and/or current dataset (values: USER, DATASET, USER_AND_DATASET). OUT: Number of rows (N) in the set, or FALSE indicating an empty set or error. |
| infoUDS_get | Get information from the current row in the current set. | OUT: Value of I_content field (single entity or XML). |
| infoUDS_put | Replace the content field in the current row. | IN: Value of I_content field (single entity or XML). |
| infoUDS_next | Define the next row in the set as the current row. | OUT: TRUE on success, FALSE if no more rows in the set. |
| infoUDS_new | Create a new row in the set and define it as the current row. The row will belong to the user and/or dataset that defines the set. If the set is only defined by user, the current dataset will be used to connect the row to a dataset. Similarly, if the set is only defined by dataset, the current user will be used. NOTE: The new row will be set up as the last row in the current set. Used inside a loop with infoUDS_next, this method will accordingly break out of the sequential visiting of rows from the set. | IN: Value of I_content field (single entity or XML). OUT: TRUE on success, FALSE on error. |
| infoUDS_delete | Delete the current row. | OUT: TRUE or FALSE indicating success or error. |
File functions
| Method | Purpose | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| file_find | Search for an existing file (owned by the curent user) and make it the current file. | IN: File name (F_name). OUT: true if found, false otherwise. |
| file_create | Create a new file (for the current user) and make it the current file. | IN: File name (F_name) |
| file_put | Set file properties for the current file | IN: Property name (one of 'F_size', 'F_status', 'F_errurl'), property value |
| file_get | Get file properties for the current file. | IN: Property name (one of F_name', 'F_size', 'F_status', 'F_errurl', 'F_timestamp'). OUT: property value |
| file_first | Make the first file (owned by the current user) the current file. | OUT: true if found, false if no files exist. |
| file_next | Make the next file in the database the current one. | OUT: true if found, false if already last file. |
| file_delete | Delete the current file entry from the database. | OUT: true if the entry was deleted, false on error. |
Example usecase
A dataset (D) has recently been updated, and a check is needed to see if this must be followed up by sending the dataset to external users as a consequence of subscriptions set up on the dataset:
new; # Open new UserBase object
dset_find D # Find dataset D in the database
# (= current dataset)
infoUDS_set SUBSCRIPTION_XML DATASET # Define the current set of rows as
# all SUBSCRIPTION_XMLs for the
# current dataset. Make the first
# row current.
Loop over the current set of rows:
user_isync # Make the current user correspond
# to the user in the current infoUDS row
# All information on the subscripion, the user that owns the
# subscription, as well as the dataset that is subscribed to, are
# now readily available as current elements.
Make necessary actions to satisfy the subscription
infoUDS_next
End loop when infoUDS_next returns FALSE
close # Close the userbase object